Let’s keep it short! From our perspective, there’s no way around a well-adjusted and tailored tube amp for the electric bass. Why is that so? What factors play a role in choosing a suitable bass amp? What fundamental differences exist in system and construction? We’ll explore all of this in this article.
Bass Amp vs. Guitar Amplifier – Similarities and Differences
In this article, we want to focus on the bass guitar amplifier and its peculiarities. At first glance, the bass amp appears to be a regular amplifier. It is designed either as a transistor amplifier or based on tubes. The unique musical role of the bass guitar in modern music necessitates some adjustments to the amplifier concept – hence the question of the best system for one’s own purpose remains relevant. Especially crucial in distinguishing between guitar and bass amps are the factors of sound and power.

Factor Sound
The roles of guitar and electric bass are very different in the modern band context. While the guitar, as a harmony instrument, is responsible for creating the melodic structure of a song, the bassist, with his instrument, moves in a world between harmony and rhythm instruments. Depending on the playing style, the focus of playing lies in rhythm accompaniment with the drums or in harmonic support of the overall melody. Most often, the bass finds itself somewhere in between and must serve both aspects – just like the bass guitar amplifier.
Therefore, the demand for the sound of a bass amp is different from that of an electric guitar and similar instruments. The frequencies of the bass guitar cover a wide range, from very powerful lows to the midrange of vocals and guitar. The tonal structure is also different from guitars and vocals – tube amplifiers are less frequently driven to distortion and overdrive.
An electric bass amplifier must, therefore, have a large headroom to accommodate the powerful, low frequencies without distortion. At the same time, for some music styles, a distorted sound is desired – this is where the natural dynamics of tubes in the amplifier come into play.
Power
Reproducing the low frequencies of a bass is the task of the bass amp. From a physical perspective, it should be noted that amplifying low frequencies requires more energy than amplifying higher frequencies. Therefore, the power of the bass amp is significantly higher than what is common in guitar amps. Bass amps can go up to 500 watts in the context of a rock band. Depending on the desired application, much lower power may be sufficient to achieve a good sound.
The power of a bass amp and a guitar amp cannot be compared! However, the process of choosing the best amplifier for one’s own purpose is similar. We will present the most important decision criteria.

Choosing the Right Bass Amp – Key Factors
As always, the selection of the right equipment depends primarily on the planned application of the amplifier. Power, design, sound, and technology of an amplifier – we provide an overview of the important criteria and give examples of applications for each electric bass amplifier.
Power According to Application
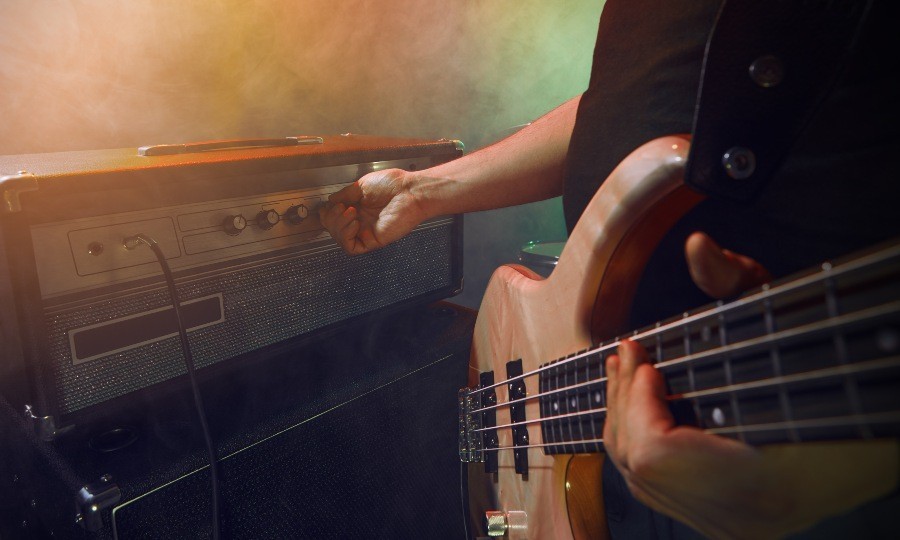
The power of a bass amp significantly influences the achievable volume, as well as the headroom of the electric bass amplifier. Headroom refers to the maximum volume a tube amplifier can reach without the tubes in the power amp distorting. For a bass amp, the power must be much higher than that of other amplifiers because reproducing and amplifying low frequencies simply requires more energy. Typical power classes for bass amplifiers, depending on the underlying technology, range from about 100 watts to 700 watts. When considering power, it is crucial to think about the intended use of the bass amp. In the full context of a rock band, it is usually recommended to use an amp with about 500 watts to compete at any time with the more assertive instruments in the midrange spectrum of the sound. In practice sessions, powers around 100 watts are often sufficient! Even in recording situations and quieter bands, lower powers can be better controlled and used. For live performances without a connected PA, 500 watts of power should be available to ensure safe handling of the bass signal.

Design
Combo or Head + Cabinets? The advantages and disadvantages of different designs of the bass amp are almost transferable from guitar amplifiers – but only almost. Here are the pros and cons of the design specifically related to the bass amp:
Combo
The combo is particularly popular among guitarists! The combination of perfectly matched speakers and amplifiers is particularly interesting for musicians who want to play a mobile system.
Unfortunately, it’s a bit different for the bass amp: While there are numerous combos for the bass as well, these, in the appropriate power class and speaker area, have little in common with the mobile, quickly transportable amps of the guitarist front. With a weight of over 30 kilograms, combos are only recommended for well-trained bassists.
However, the advantages of the perfectly matched technology and the more affordable purchase prices of the bass amp combos remain.
Head + Cabinets
The combination of head and cabinets as a bass amp is interesting for all bassists who want to build their setup modularly and unfold the full strength of the amp and speakers.
Due to the different combination options, this setup provides greater freedom in sound design. With a head and individual speaker cabinets, there are hardly any limits.
On the other hand, the purchase of a head and speakers is quite expensive and not easy to transport… but the drummer will surely help with the transport of the bass amp!
Sound
When it comes to sound, the musical taste of the bassist is particularly decisive: If clear clean sounds are desired, attention should be paid to sufficient headroom, and accordingly, “quieter” preamps should be selected. Especially in metal and rock, the bass is often played distorted – here, a correspondingly hot amp is called for and can be further heated up with effects.
Attention: With bass guitars, much can be achieved through the type and size of the used speakers. Experimenting with bass guitar amps and speakers is mandatory here!
Technology
Nothing beats tubes! Dynamic, natural sounds with deep warmth and natural distortion make the bass amp with tubes stand out. The arguments here can be transferred from guitar and similar instruments to the bass amp in principle.
In the case of the bass, the power of tube technology is to be emphasized – here, 500 watts of power from the tube provide much more strength than a comparably sized transistor amp with a corresponding power amp. But even these have an advantage over tube amplifiers! The comparatively larger headroom is appreciated by bassists who prefer a more analytical clean sound.
In our opinion, the better, more natural, and above all, more musical results can be achieved with a appropriately sized tube amplifier!
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Image sources:
Featured image: © Voloshyn Roman – stock.adobe.com
Bassist in the rehearsal room: © Nomad_Soul – stock.adobe.com
Bassist and saxophonist on stage: © evannovostro – stock.adobe.com
 Tubeampdoctor Magazin
Tubeampdoctor Magazin